Basic Life Support.(BLS)
Basic life support (BLS) is a set of emergency medical skills that anyone can learn to help someone in a medical crisis. It typically includes CPR, choking rescue, and basic first aid techniques. The goal of BLS is to stabilize a patient until advanced medical help arrives. It’s like the first responder skillset – no fancy equipment or years of medical training required!
Here are a few more key concepts in BLS:-
- Assessment of the patient’s condition, including checking for responsiveness, breathing, and circulation.
- Calling 911 and providing accurate information about the patient’s condition.- Maintaining a safe environment for the patient and bystanders.
- Providing emotional support and reassurance to the patient and their loved ones.
- Continuous monitoring of the patient’s condition and adjusting interventions as needed.Pretty rad stuff, if you ask me!
CPR 101:The Basics of Chest Compressions and Rescue Breaths.
“CPR 101: The Basics of Chest Compressions and Rescue Breaths.” Here’s the opener: “CPR – it’s not just for lifeguards and EMTs anymore. In fact, everyone should know the basics of this life-saving technique. Whether you’re at home, work, or out in the world, being able to perform CPR could mean the difference between life and death for someone in need.
How to performe Chest Compressions and Rescue Breaths
- Chest Compressions: Place the heel of your hand on the center of the chest, interlock your fingers, and push down hard and fast at a rate of 100 to 120 compressions per minute.
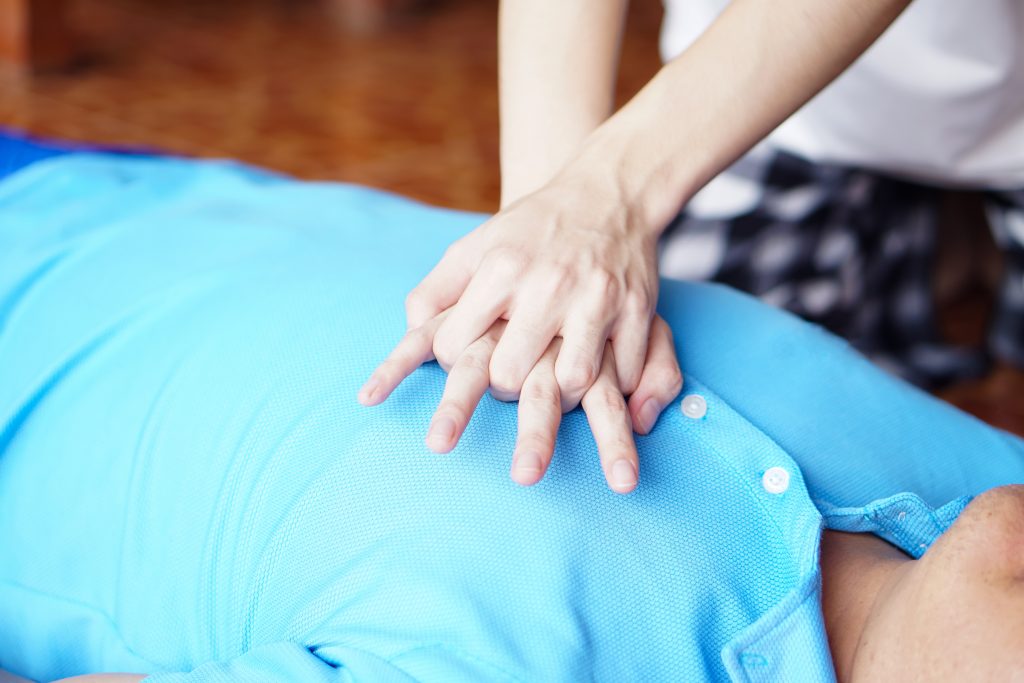

GIVING CHEST COMPRESSIONS
Rescue Breaths: Tilt the head back and lift the chin to open the airway. Pinch the nose closed and blow into the mouth to inflate the lungs with two full breaths.
Repeat the cycle of 30 compressions and two breaths until advanced medical help arrives or the patient begins to breathe on their own.
AEDs: The Lifesaving Technology you need to know.
AEDs, or automated external defibrillators, are portable, electronic devices that deliver a controlled electric shock to the heart to restore a normal heartbeat in someone experiencing cardiac arrest.
- They’re easy to use – most AEDs provide step-by-step instructions and voice prompts.
- They can analyze the heart’s rhythm and determine if a shock is needed, making them safer and more effective than manual defibrillation.
- They can increase the chances of survival by up to 75% when used within the first few minutes of cardiac arrest.
- AEDs are often found in public places like airports, malls, and schools, and they’re designed to be used by anyone – no medical training required.
- AEDs are relatively affordable, and many states have passed laws requiring them in certain public spaces.
- Studies have shown that AEDs can even be used successfully by children as young as 10 years old, making them an important tool for community safety.
Types of AEDs
There are three main types of AEDs:
- Automated AEDs: These provide audio and visual prompts and administer the shock automatically.
- Semi-automatic AEDs: These provide prompts but require a user to press a button to deliver the shock.
- Manual AEDs: These require a trained operator to interpret the heart rhythm and decide when to deliver the shock.Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, but they all have the same goal – to save lives!
Emergency Recognition: Spotting The Signs Of Crisis.
Emergency comes in all shapes and sizes, but there are some common signs to look out for when spotting crisis. These Includes
- Rapid or labored breathing
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or fainting
- Confusion or disorientation
- Severe bleeding
- Seizures or convulsions
- Changes in skin color (e.g., paleness, blueness, or yellowing)
- Severe pain
- Changes in mental status (e.g., slurred speech, incoherence)Those are some red flags to look out for!
* Rapid or Laboured Breathing:
Rapid or labored breathing, also known as dyspnea, refers to difficulty breathing or shortness of breath. Symptoms include:
- Chest tightness or pressure.
- Wheezing or crackling sounds when breathing.
- Shallow or irregular breathing patterns.
- Feeling like you can’t get enough air.
- Gasping or struggling for breath. These symptoms can be caused by a range of medical conditions, including asthma, heart failure, pneumonia, and anxiety.
- If you or someone around you experiences rapid or labored breathing, it’s important to seek medical attention right away, because it can be a serious medical emergency.
* Chest Pain or Discomfort.
Chest pain or discomfort is a common symptom that can indicate a variety of medical conditions, including:
- Heart attack: The most serious cause, characterized by a crushing, squeezing, or burning sensation in the chest.
- Angina: A type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Pulmonary embolism: A blood clot in the lung that can cause chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the lining around the heart that can cause chest pain and shortness of breath.
* Dizziness or Fainting:
Dizziness and fainting are no joke! They can be caused by a range of issues, such as
- Dehydration- Low blood pressure-
- Heart problems
- Panic attacks
- Low blood sugar
- Heatstroke
- Medication side effects
- The key to managing dizziness or fainting is to try to prevent it. Staying hydrated, getting enough rest, and avoiding excessive heat can help. And if you feel dizzy or faint, sit or lie down and elevate your feet to improve blood flow to the brain.
* Confusion and Disorientation:
Confusion and disorientation can be unsettling. They can be caused by various things, such as:
- Head trauma or concussion
- Stroke or TIA (transient ischemic attack)- Infections like meningitis or encephalitis
- Medication side effects or drug interactions-
- Dementia or Alzheimer’s disease
- Low blood sugar or dehydration
- Seizures
- Anxiety or panic attacks
- The key is to stay calm and try to get help if the confusion is severe or persistent.
* Severe Bleeding
Severe bleeding can be scary, but it’s important to stay calm and act fast. Here are some key tips:-
- Apply direct pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage.
- Elevate the affected area above the heart to slow the flow of blood.
- Apply pressure to nearby pressure points to slow the bleeding.
- Apply a tourniquet (if trained) as a last resort to stop severe bleeding.
- Call 911 or emergency services ASAP!
* Seizures or Convulsions:
Seizures and convulsions can be intense! Here are some tips to help someone experiencing a seizure:-
- Do NOT restrain the person or put anything in their mouth.
- Keep them safe from injury by gently cushioning their head and protecting them from falls.
- Stay with the person and talk calmly until the seizure ends.
- Time the seizure (how long it lasts) and note any changes in their breathing or skin color.
- Once the seizure stops, help the person recover and get medical attention as soon as possible.
* Changes in Skin Colour
Skin color changes can be a warning sign of something serious. Here’s what to look out for:
- Pale or white skin can indicate shock or low blood pressure.
- Blue or gray skin can be a sign of poor circulation or lack of oxygen.
- Red or flushed skin can be a sign of fever, infection, or allergy.
- Yellow skin can be a sign of liver problems or jaundice. Any of these changes can be serious, so it’s important to pay attention and get medical help if necessary.
* Severe Pains:
Severe pain can be a major red flag, and it’s important to get help right away. Here are some common causes:
- Broken bones or fractures- Kidney stones or gallstones
- Infections like appendicitis or pneumonia- Nerve damage or pinched nerves
- Heart attack or stroke
- Gastrointestinal issues like appendicitis or ulcersSevere pain can be really scary, but it’s always important to get medical help to figure out what’s causing it. Delaying treatment can sometimes make things worse!
* Change In Mental State(Slurred Speech and Incoherence)
Some things that can cause changes in mental state include:
- Stroke or brain injury
- Medication side effects or drug interactions
- Mental health issues like depression or bipolar disorder
- Neurological conditions like dementia or Alzheimer’s disease
- Infections or illnesses that affect the brain, like meningitis or encephalitisChanges in mental state can be really tough, not just for the person experiencing them but also for their loved ones. It’s always best to get medical help to figure out what’s going on and find the right treatment.
Choking Emergencies: A comprehensive guide to Heimlich Maneuver and other Techiques.
Let’s talk about choking emergencies! They can be scary, but knowing how to respond can save a life.
The Heimlich maneuver is the most well-known technique:
- Stand behind the choking person and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist with one hand and place it just above the person’s belly button.
- Grasp your fist with the other hand and give upward and inward thrusts until the object is dislodged.
- If the Heimlich maneuver fails, alternate with back blows and chest thrusts until help arrives.
Other Techniques:
Other techniques to try include:
- The self-administered Heimlich maneuver, where you use your own hands to dislodge an obstruction.-
- Back blows, where you hit the choking person between the shoulder blades with the heel of your hand.
- Chest thrusts, which are similar to the Heimlich maneuver but performed on infants and small children.-
- The “head-down tilt,” which can be used in situations where the person is unconscious.
- These techniques can be complicated, so it’s important to receive proper training before attempting them.
Unconscious and Recovery position: keeping patient safe and stable:
The recovery position! Here’s the deal:
- If someone becomes unconscious, it’s important to keep their airway clear and ensure they are breathing normally.
- The recovery position is a way to position an unconscious person on their side to prevent them from choking on vomit or saliva.
- To put someone in the recovery position:- Turn them onto their side, with the ear closest to the ground resting against the ground.
- Bend the top leg at the knee, and gently tuck it behind the knee of the bottom leg.
- Ensure the person’s head and neck are supported.
- Check for any signs of injury, such as cuts or bruises.
- Keep the person warm and monitor their breathing and pulse.
- If the person vomits, turn them onto their side or stomach to prevent choking.
- DO NOT give the person anything to eat or drink, even if they seem conscious.And of course, if someone is unconscious, always call emergency services immediately.
The bottom line:
“Basic health support is a key component of maintaining overall health and wellness.
Being aware of potential health issues and taking preventative measures, such as practicing healthy habits, getting regular check-ups, and seeking medical attention for any concerning symptoms can go a long way in staying healthy. By being proactive, we can improve our quality of life and reduce the risk of developing serious health problems.
Remember, your health is your most valuable asset – take care of it!”

0 Comments